Commercial vehicles play a key role in the global economy, transporting goods around the world and assisting in the development of infrastructure. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced a proposal in 2023 to revise the current standards that aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with commercial vehicles and set new, more stringent standards. Meeting these ambitious targets requires major change. As a result, businesses of all sizes in this industry need to rethink how they operate.
Custom Truck One Source is a leading all-in-one provider of trucks and specialty equipment, and we are committed to driving sustainable solutions for a greener future. Below, you can learn more about our environmentally friendly initiatives and how we are encouraging change across the industry.
Custom Truck One Source’s Green Initiatives
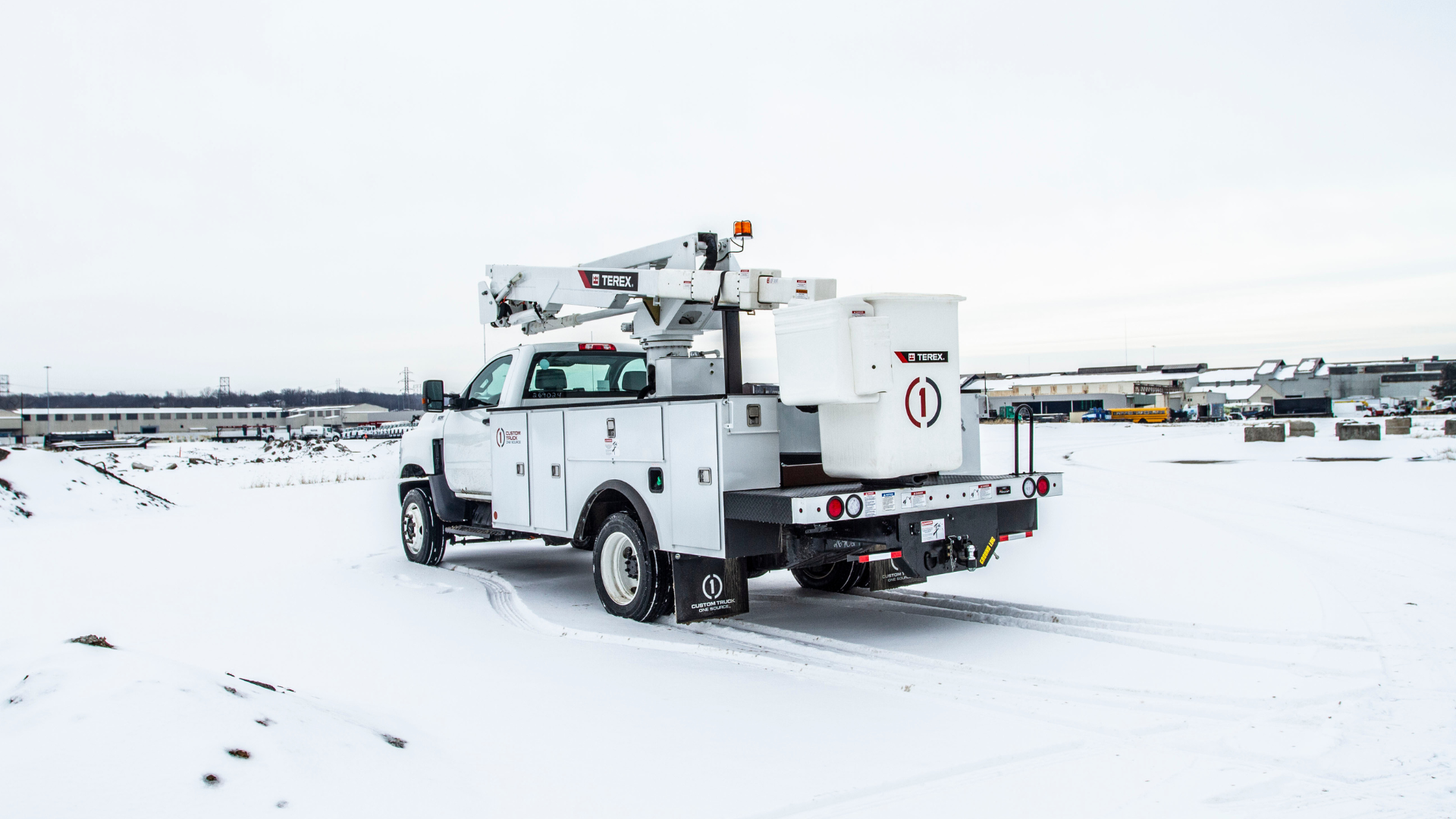
At Custom Truck One Source, we strive to help solve emission regulation challenges with our electric and electric-hybrid chassis line. Load King Lighting PTO, an electric power take-off, is an electric alternative designed to power hydraulic systems responsible for operating utility equipment. This innovation ensures the vehicle’s engine only runs during transportation and offers hybrid compatibility, allowing charging through standard 110AC outlets. It can charge while the diesel chassis is in use.
We’ve integrated this innovative technology into various types of equipment. The advantages of Lightning PTO include:
- An average of 2,000 gallons of diesel fuel savings per year
- A reduction of roughly 44 tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions per year
- An 85% noise reduction for quieter work environments
- Less wear and tear caused by hydraulic oil movements
- A decreased need for vehicle maintenance
- Minimal idle regulation compliance
While the major reductions in diesel fuel use and CO2 emissions are valuable benefits, this technology can reduce maintenance costs significantly. Investing in this technology for your fleet will translate into notable long-term cost savings.
A high-tech telematics and reporting dashboard enables customers to collect data on fuel savings, emission reductions and even decreasing maintenance needs. The telematics dashboard makes it possible to track fleet locations efficiently and monitor battery levels to ensure they never run flat. This technology has the potential to transform the commercial vehicle industry and positively influence climate change.
Technological Innovations
Lightning PTO is powered by the 48V 5kWh commercial battery (Fi5.0) from IFP Motion Solutions and Vanguard, allowing customers to operate the hydraulics system without having to run the engine, which translates into fuel savings. This powerful battery offers the right amount of runtime and recharge capabilities for the technology.
The increasing need for power helped engineer a newer model that incorporates the 48V 7kWh (Fi7) battery. With this, the Lighting PTO delivers more capacity without increasing its carbon footprint.
Beyond Lightning PTO, other new technologies are shaping fuel delivery for the better. Some portals and apps make it easy to order fuel online. At the same time, cloud-based software solutions, mobile technologies, customer relationship management software and tank monitoring systems are all innovations that can help the industry achieve better sustainability.
Collaborations and Partnerships
Our partnership with Battle Motors, an electric vehicle and commercial equipment manufacturer, adds their full line of electric trucks to our inventory to offer customers more value. With this inspiring industry leader at our side, we also offer California Air Resources Board emissions compliance solutions for all sales and rentals, which is especially beneficial to municipal and refuse markets.
In 2018, we partnered with Cusco, a manufacturer of quality vacuum trucks for industrial, commercial and environmental use. Cusco has over five decades of experience as an industry leader. The company’s truck-mounted vacuums remove hazardous and non-hazardous waste, contributing to pollution reduction measures. With the partnership, contractors across the United States can access quality Cusco Turbovacs, Hydrovacs and industrial vacuum trucks through our lease, rental and purchase options.
We’ve also partnered with Hi-Vac Corporation to become an authorized dealer of Hi-Vac Corporation’s products. Hi-Vac Corporation focuses on sustainability as a core value. For over four decades, they’ve been providing quality products and services that address infrastructure, maintenance and cleanup challenges around the globe.
Other partnerships we have include Toro, EZ Trac, Ring-O Matic, Tornado Global Hydraulic, UTV International, Terex Utilities, Posi Plus Technologies and a few others. Our strategic partnerships with these experts enable us to continue to develop green transportation solutions to mitigate the sector’s carbon footprint.
Sustainability Challenges and Opportunities in the Commercial Vehicle Industry
Striving toward sustainability is not without its challenges — but these challenges are all opportunities for growth and new, improved sustainable solutions. From meeting ambitious emissions targets to reducing pollution and improving recycling efforts, here are the primary challenges the commercial vehicle industry faces.
Meeting Emissions Targets
The biggest challenge for the commercial vehicle industry is reducing emissions in accordance with EPA standards. As a result, many automakers are adding electric and hybrid vehicles to their fleets. Drone technology offers another solution, as these devices can reduce the number of delivery drivers on the roads.
The technology required to comply with these regulations serves as a challenge. Mechanical ingenuity is essential for sustainable vehicles to emit fewer fumes. Between emission-controlling devices, new operating strategies, the use of fossil fuels and hybridization, automakers and manufacturers need to develop technologies that can combat these challenges.
Beyond the challenge of developing these innovations, implementing them is another challenge. Businesses need to invest when altering operations and equipment, and not all businesses have the funding available. At Custom Truck One Source, we offer in-house financing solutions to ensure our customers can make sustainable changes that will benefit the environment.
Improving Air Pollution
Despite major strides in electrifying vehicles, it’s unlikely that gasoline and diesel use will dissipate anytime soon, so improving air pollution remains a challenge. However, regulatory bodies are taking steps to encourage and require businesses to choose zero-emissions alternatives.
For example, the California Air Resources Board has recently proposed Advanced Clean Fleet regulations. In the coming years, California fleets must phase out traditional combustion engine vehicles and upgrade them to zero-emissions vehicles by 2036. After that, all medium and heavy-duty truck manufacturers in the state may only produce zero-emissions vehicles.
Industry leaders are also developing other clean air solutions to reduce pollution. Three-way conversion technology can convert three types of pollutants — hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxide — into safe gases. Advanced radiator applications can also convert harmful ground-level ozone into harmless oxygen. Ground ozone is a main component of smog, which has significant environmental impacts. These technologies are shaping a greener, cleaner future for all.
Meeting Recycling Targets
In addition to strict emissions goals, the commercial vehicle industry must also find solutions to meet recycling targets. Many new directives and regulations around the world are encouraging the adoption of a circular economy. Automakers and manufacturers must reduce their contribution to landfills by implementing forward-thinking recycling solutions. Through the right recycling processes, plastic and metals like platinum and rhodium can be recycled and reused.
When recycling initiatives are in full swing, automakers and manufacturers can essentially manufacture new products from old products, leaving behind less waste for landfills. However, implementing these recycling initiatives requires time and money, which poses a setback for some companies.
Additionally, lithium-ion batteries present a challenge in sustainability, namely when it comes to mining and disposal. Mineral extraction for lithium-ion batteries can lead to erosion and pollution, and current waste disposal methods generate toxic by-products that harm human health and the environment. Additionally, there is rising concern regarding abandoned batteries. Fortunately, steps are being taken to recover materials from used batteries and recycle the batteries themselves — the battery recycling market is expected to be worth $35 billion by 2031.
Automotive industry leaders need to work together to find recycling solutions that overcome these pressing challenges. Further, over the next decade, we will likely see breakthroughs in battery recycling technology to manage battery waste more effectively.
Understanding Sustainability Strategies
Between business owners, their fleets and their employees, everyone must understand why sustainability matters. Investing in a new line of electric or electric-hybrid vehicles can support change, but it’s still vital that employees receive sustainability training that informs them of green practices.
Sustainability training is a solution that will equip employees with the right skills and knowledge to implement effective steps and processes in their work. From energy conservation to waste reduction and recycling, your entire team should be on board. These training programs are an accessible way to empower employees.
With this, there’s also an opportunity to empower individuals to drive change in their lives outside of work. With a better understanding of sustainability and how to achieve it, employees become more conscious of their impact on the environment and can enforce green practices at home, as well.
Impact on the Industry and Beyond
As Custom Truck One Source continues to develop and release innovative sustainability solutions, the wider commercial vehicle industry can adopt these new technologies. By retailing commercial vehicles and equipment that have a reduced impact on the planet, customers and auto dealers can benefit from decreased emissions, lower fuel costs, and more.
In construction, air pollution, water pollution, land erosion and chemical pollution are major concerns. With the right equipment, the construction industry can reduce its carbon footprint. Further, when it comes to the forestry industry, deforestation and degradation of natural forests are concerns. Restorative forestry encourages the rehabilitation of degraded lands. We offer quality equipment that plays a vital role in forest rehabilitation, from forestry trucks to logging equipment and more.
The railway industry is another sector that benefits from our sustainable solutions. Between automation and reduced emissions, this industry has a greener outlook. Municipal services also benefit from our range of equipment geared at waste removal and environmental cleanup.
Future Directions
While the commercial vehicle industry is making notable improvements, there’s still a long way to go. However, as more businesses and customers get on board with sustainability goals, new solutions continue to emerge and enact change.
With the rise of artificial intelligence and automation, we can expect autonomous vehicles to impact sustainability soon. Data is becoming an integral part of the logistics industry. With smarter and newer software solutions, accurate data and valuable insights can help businesses make decisions considering the environment.
Big data and predictive analytics will likely also influence new developments while adopting multichannel logistics offers the industry a trend that could spark more interest in sustainable changes. Beyond these predictions, hybridization in logistics strategies is already here, although we can expect these strategies to be adopted on a larger scale.
Learn More About How Custom Truck One Source Supports the Green Movement
Custom Truck One Source emerged in 1996 as a small family business. Today, we have expanded to over 2,400 employees, and our central headquarters now occupies a 75-acre site. We continue to expand our organization to continue to support industries across North America. Currently, our 35 locations span across the United States and Canada.
We offer sustainable specialty trucks and custom equipment for forestry services, construction and infrastructure, railway, municipal services, and more. We are trusted by over 3,000 customers who rely on our products for their businesses. We assemble, sell, rent, and service trucks and other heavy vehicles and equipment as a one-stop shop for all your trucking needs. Our wide range of products, skilled experts, and network of partners are focused on delivering unmatched value to our customers.
As an industry leader, we do what it takes to enact environmental responsibility across our equipment and services. With our green initiatives like the Lightning PTO system, we are helping reduce emissions for the wider industry. By collaborating with other experts who are focused on sustainability, we can continue developing powerful green initiatives.
Learn more about our products and how we encourage industry change. Contact us today to request a quote or make an inquiry.